class a foam acts as a surfactant which means that it
AFFF Aqueous Film Forming Foam. Class A foam is used for Class A fires which include solid combustibles such as paper wood cloth and some plastics.

Surface Active Agents Surfactants Types And Applications
An example would be like cooling a glass of water with a single ice cube.
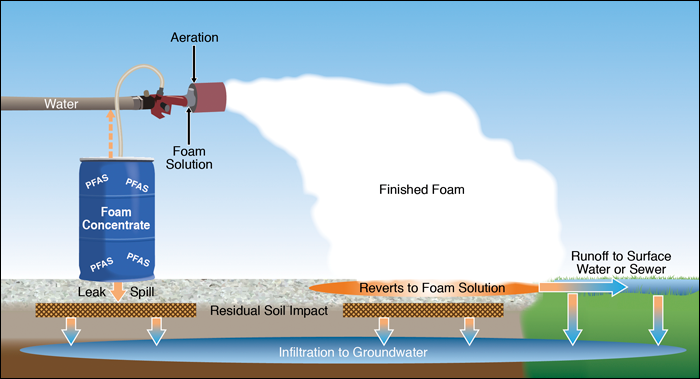
. Class B foam is used on flammable liquids. A foam concentrate containing fluorochemical surfactants that control the physical properties of water enabling it to float and spread across the surface of the hydrocarbon liquid. In particular AFFF manufactured by the 3M Corporation sold prior to.
Anionic surfactants have a negative charge on their hydrophilic end. The fluorinated surfactants used in AFFF are produced by one of two synthetic processes 1. Class A Foam Wildland Foam Class AB Foam Pyrocool Aqueous Film Forming AFFF Class A Foam Wildland Foam The foam is a non-corrosive non-toxic biodegradable concentrate.
Class A foam is for use against Class A fires such as paper rubber textiles and wood. In addition the portion of the foam concentrate molecule that repels other water in order. They are also used extensively in industry.
PFOA and PFOS form a class of chemicals called perfluorinated compounds PFCs that act as surfactants to improve the effectiveness of Class B firefighting foams in fighting petroleum and other fires. Costs for training Most departments did not quantify the cost of training their personnel to operate class A foam systems. This is nothing to do with drainage as explained in Drainage the walls contain an irrelevant.
Class A Foam vs. CLASS A FOAM CONCENTRATE. They are added to remove dirt from skin clothes and household articles particularly in kitchens and bathrooms.
Wetting and emulsifying TERGITOL Surfactants deliver low foam excellent solvency chemical stability and reliable formulation performance in a number of fermentation food processing. Class A foams are often intended for use at very low concentration of 01 to 1 and are formulated using environmentally favourable raw materials. CAFS units may cost up to 40000 per vehicle.
Global supply from world-class manufacturing facilities. Class A foam will increase wetting effectiveness. These are prepared by direct electrochemical fluorination.
Difference was noted with nozzle-aspirated class A foam. Dow produces surfactants that act as emulsifiers dispersants wetting agents for crop. As a fire barrier Class A foams increase moisture con-tent in Class A combustibles preventing the ignition of these type fuels.
As foam generation and also foam stability is a dynamic for process for generating and reducing surface area in a surfactantwater system the diffusion of the surfactant to the surface and the change in surface coverage at least locally during bubble generation and drainage of the film is a more useful way of explaining foam properties. Because they are able to attack a broad range of soils anionic surfactants are used frequently in soaps and detergents. Class A foam typically runs at 03 05 or 1.
Many Class A foams are environmentally friendly and biodegradable when used in appropriate quantities. Environmentally responsible KnockDown a Class A foam concentrate is a unique formulation providing unmatched firefighting performance and flexibility. Class A foam is primarily a surfactant which is to say that it breaks down the surface tension of water.
Figure 1 Surfactants aid the effective. Anionic surfactants create a lot of foam when mixed. It reduces the surface tension of the water and.
The second reason that surfactants help create foam is that the liquid in the foam walls is naturally sucked out of the walls into the edges. When mixed in correct proportions with water it can change two properties of the water. The term surfactant comes from the words surface active agent.
Aqueous film forming foam AFFF means a fluorinated surfactant with a foam stabilizer which is diluted with water to act as a temporary barrier to exclude air from mixing with the fuel vapor by developing an aqueous film on the fuel surface of some hydrocarbons which is capable of suppressing the generation of fuel vapors. National Foams Class A Foams are also wetting agents. One class of fluorosurfactants used in AFFF formulations is based on perfluorooctyl sulfonate PFOS and structurally related compounds.
When mixed in correct proportions with water it can change two properties of the water. When added to water the resulting foam solution consists of many smaller droplets with much more surface area allowing faster heat absorption. When mixed with water in the correct proportion it changes the properties of water.
Class A Foam. Surfactants are one of many different compounds that make up a detergent. This is a biodegradable mixture of foaming and wetting agents.
Costs of equipment Departments reported equipment costs up to 5000 per unit for nozzle-aspirated class A foam systems. Anionic surfactants are the initial and most developed and the leading class in several forms of surfactants. Water Foam Class A concentrate is simply a surfactant similar to dishwashing soap that reduces surface tension.
Class A foam is used on common combustibles such as paper wood and textiles. When used as a wetting agent the concentrate lowers the surface tension of the water allowing better penetration into deep seated fires. The negative charge helps the surfactant molecules lift and suspend soils in micelles.
They may be broadly employed as foaming agents antistatic agents dispersants detergents emulsifiers and stabilizers in the biochemical features of life 29. Class A foams are blend of surfactants that enable strong wetting and foaming properties. This is a biodegradable mixture of foaming and wetting agents.
Class A foams may be used as a firefighting agent or as a fire barrier. Qualified to USDA Forest Service 5011-307a and UL approved for use as a wetting agent for Class AB applications Environmentally responsible.

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

Ingredient Spotlight Surfactants
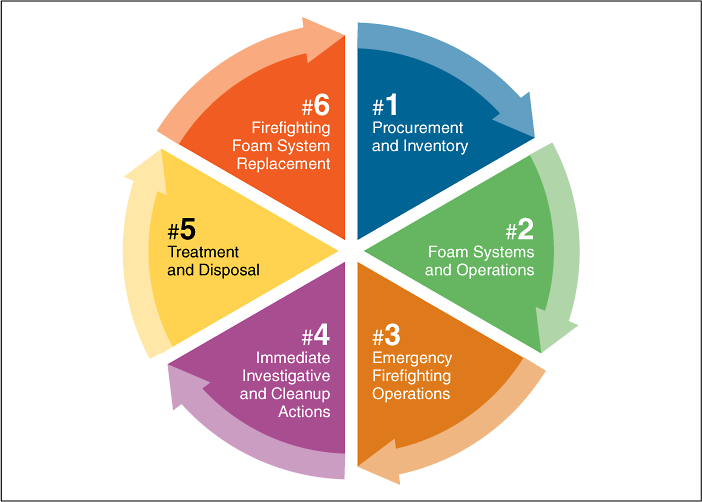
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

Stability Of Foam An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex
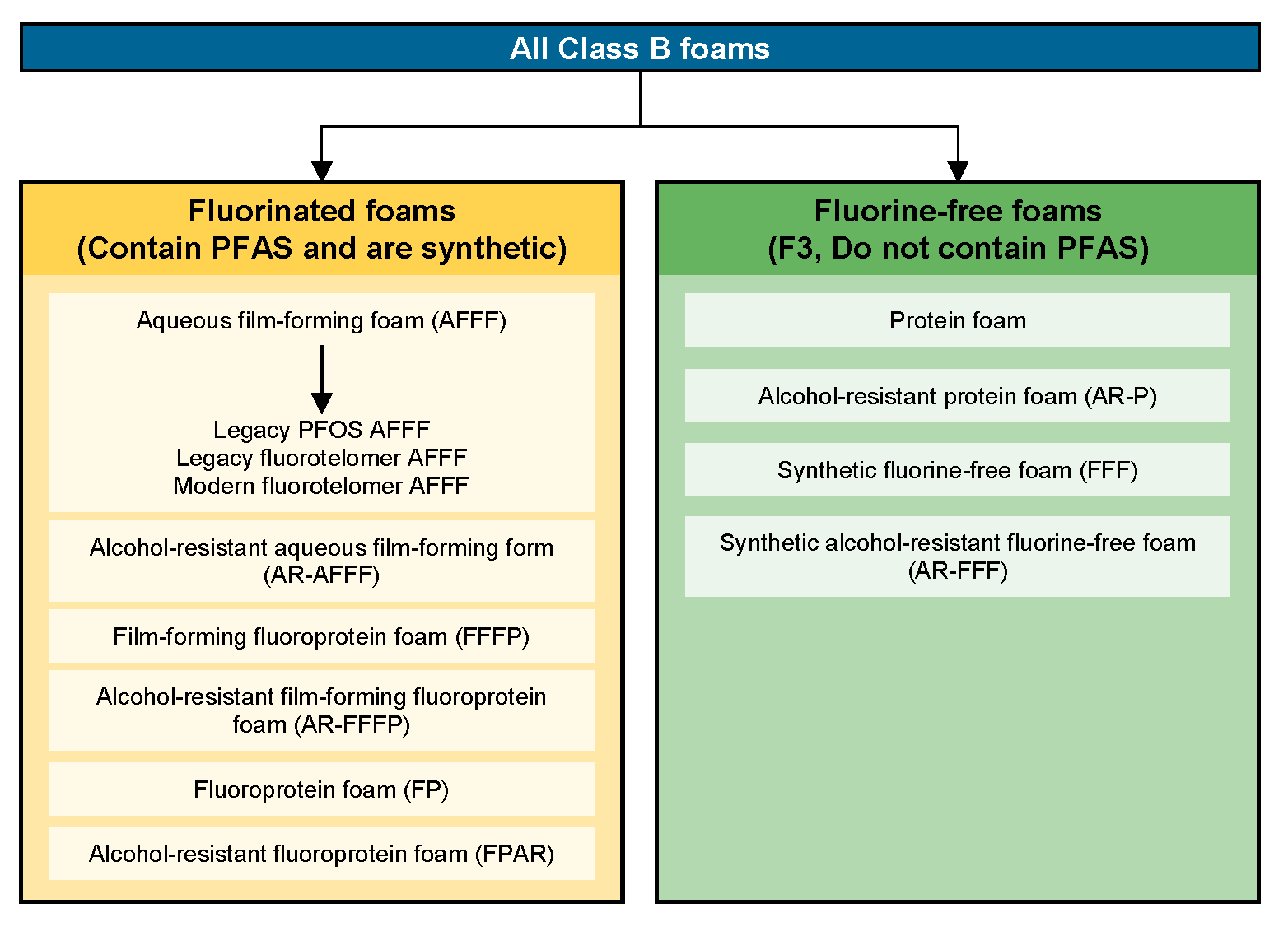
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances